Subcutaneous injection protocol
This protocol is a draft. It has not yet been accepted as protocol and may be incorrect or poorly cited. Please do not use this in your work until it has been accepted.
Please see #protocols on Slack to discuss this protocol further.
This document needs review by medical professionals before it is adopted. If you are a medical professional, please use this form to provide feedback
More documents in need of medical review can be found here.
This is a protocol for (self-)administering a subcutaneous(often "SC" "or "subcut") injection. This protocol is most commonly used for administering decapeptyl, a GNRH analogue, in HRT, or insulin, for the treatment of diabetes.
Contents
When to do a subcutaneous injection
Subcut injections should carried out by a clinical professional, most often a nurse, however this is not an option(as has been becoming more common through the Covid-19 pandemic) then they can be self administered or administered by others, with the patientc consent.
What to do before doing a subcutaneous injection
- You must explain the procedure, if you're doing it to a different person, and gain their consent for you to do it to them.
- You must check the medication is correct. Talk to the patient and check if it's:
- The right medication- Check the medication labeling to ensure it's what you expect to be in the bottle, and consider substance testing.
- The right dose- check the dose is what is intended.
- The right time(and date)- decapeptyl is normally on a three or 6 month cycle, insulin twice or more a day.
- The right route- Check it's not an IM or IV injection, for example.
- The right person- Talk to the person, make sure they're expecting the medication and that they recognise the medication as medication intended for them.
- You should clean an area to work on(if you cannot, make sure not to let the needles touch any surfaces that have not been sanitised), with an alcohol or antibacterial wipe, and lay out:
- A sharps bin
- The medication
- A long(3cm+), wide(commonly 18 gauge), and possibly blunt needle for drawing up drawing up
- A shorter(commonly 4-8mm long) and thinner(normally 25 or higher gauge) needle for doing the actual injection.
- Alcohol swabs
- Any PPE
- You must put on any relevent PPE, which should include gloves, but given this protocol will not normally release blood or other bodiliy fluids, you can choose not to.
- You must clean your hands, with soap and water or alcohol hand gel.
- Draw up the medication
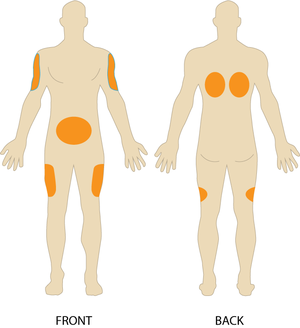
- You must select a site for an injection:
- Talk to the patient and ask them their prefered injection site- the outsides of the upper arm and the front of the thighs are normally the best options, but any site in fig 1 can be used.
- Look at the injection site and check it's clean and free of infections, scars, leisons, and other markings, as well as muscle or bone close to the surface- the aim is to inject into the layer of fat below the skin("subcutaneous fat").
- You must clean the injection site, with an alcohol swab, for 30s or more.
How to do a subcutaneous injection
- You must tell the person you're going to inject them, and talk to them about distracting things if it's nessecary.
- You must pinch the skin and the fat(but not the muscle) to make it easier to insert the needle into.
- Holding the injection like a pencil, push the needle just below the surface, until it's penetrated the skin and rests in subcutaneous fat.
- You must draw back on the plunger a little, and check no blood appears in the syringe. If it does, repeat at a slightly different site.
- Inject the contents of the syringe over 10-30s
- You must wait 10s and then withdraw the needle
- You must release the pinch of skin and fat.
What to do after do a subcutaneous injection
- Place the needle in a sharps bin, throw the syringe in a black bin(or clinical waste bin if one is available)
- Check in with the person receiving the injection, and make sure you and they have a note of the medication and time it was administered